What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Stems cells divide to form daughter cells.
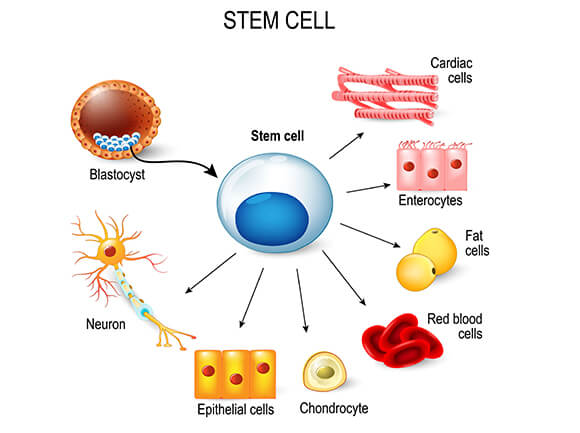
These daughter cells either can then become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells, or bone cells, or any other type of cell.
Where Do Stem Cells Come From?
Researchers have discovered several sources of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells. These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells.
- Adult stem cells. These stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat. Compared with embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited ability to give rise to various cells of the body.
- Adult cells altered to have properties of embryonic stem cells (induced pluripotent stem cells). Scientists have successfully transformed regular adult cells into stem cells using genetic reprogramming. By altering the genes in the adult cells, researchers can reprogram the cells to act similarly to embryonic stem cells.
- Perinatal stem cells. Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells.
Why is there such an interest in stem cells?
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur. By watching stem cells mature into cells in bones, heart muscle, nerves, and other organs and tissue, researchers and doctors may better understand how diseases and conditions develop.
- Generate healthy cells to replace diseased cells (regenerative medicine). Stem cells can be guided into becoming specific cells that can be used to regenerate and repair diseased or damaged tissues in people.
Have stem cells already been used to treat diseases?
Yes. As of 2019, cord blood therapies are the only FDA approved, stem-cell based therapies in the United States. These cord blood therapies are currently limited to treating patients with blood disorders. Stem cell based injections can be used to treat off label conditions, such as damaged joints from osteoarthritis.
Researchers are testing adult stem cells to treat other conditions, including a number of degenerative diseases such as heart failure.
